What is IVF or In Vitro Fertilization?
In 1978, the world’s first baby was born through In Vitro Fertilization or IVF. Her birth revolutionized the field of reproductive medicine. Given that approximately 1 in 8 heterosexual couples has difficulty conceiving, and that homosexual couples and single parents often need clinical help to make a baby, the demand for IVF has been growing. This artificial procedure became so popular that more than 5 million babies have been born through this technology.
How is the Baby Made the Natural Way?
In order to understand IVF Treatment, we first need to take a look at the natural process of baby making. Roughly 15 days before fertilization can happen, the anterior pituitary gland secretes Follicle Stimulating Hormone or FSH, which ripens a handful of follicles of the ovary that then release estrogen. Each follicle contains 1 egg and on average, only 1 follicle becomes fully mature. As it grows and continues to release estrogen, this hormone not only helps coordinate growth and preparation of the uterus, it also communicates to the brain how well the follicle is developing.
When the estrogen level is high enough, the anterior pituitary releases a surge of Luteinizing Hormone (LH), which triggers ovulation and causes the follicle to rupture and release the egg. Once the egg leaves the ovary, it is directed into the Fallopian tube by the finger-like Fimbriae. If the egg is not fertilized by sperm within 24 hours, the unfertilized egg will die, and the entire female reproductive system will reset itself, preparing to create a new egg and uterine lining the following month.
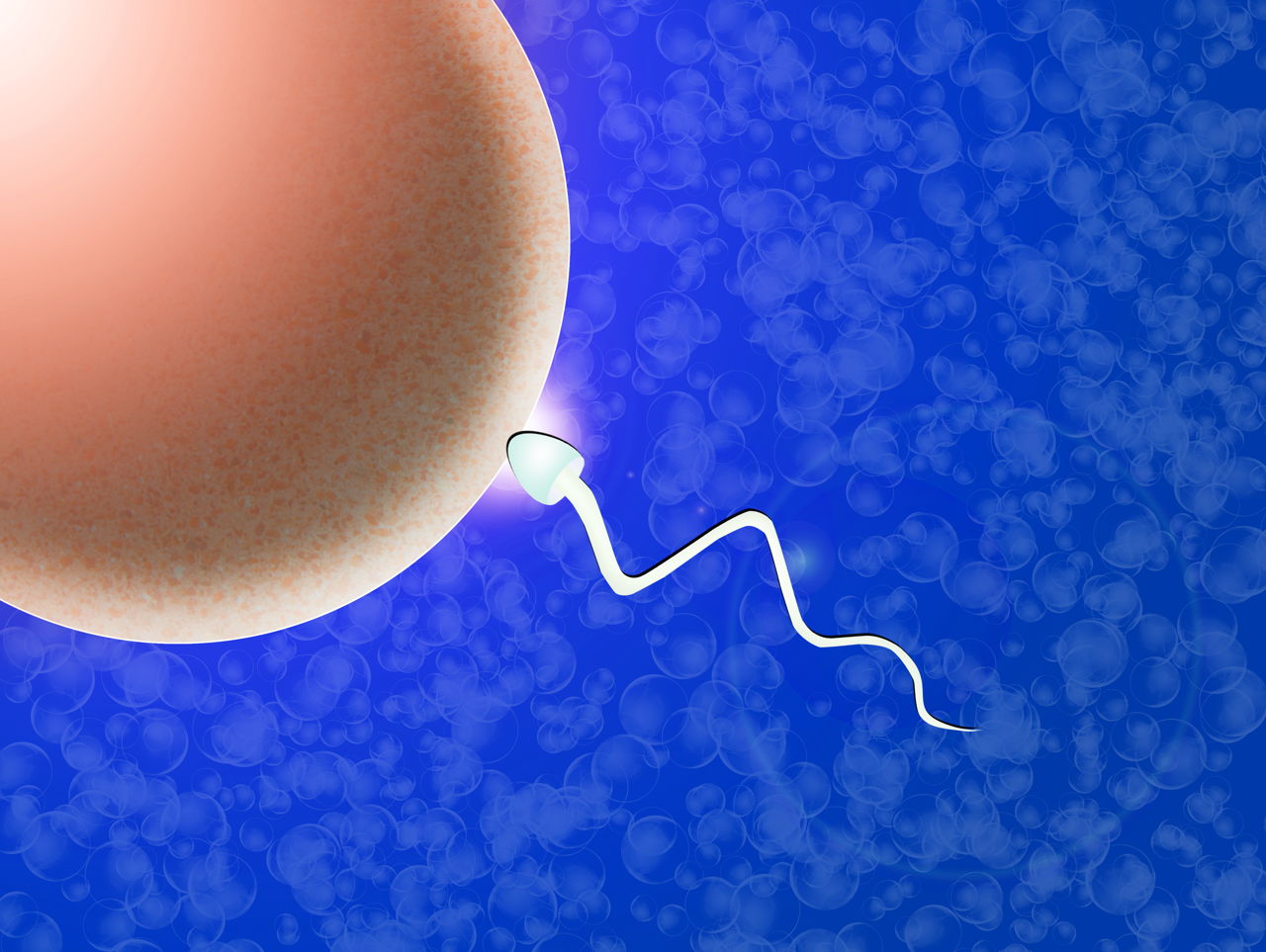 The egg is the largest cell in the body and is protected by a thick extracellular shell of sugar and protein called the Zona Pellucida. This protective lining thwarts the entry of more than 1 sperm, which is the smallest cell in the body. It takes a man 2 to 3 months to make a sperm, then the process constantly renews.
The egg is the largest cell in the body and is protected by a thick extracellular shell of sugar and protein called the Zona Pellucida. This protective lining thwarts the entry of more than 1 sperm, which is the smallest cell in the body. It takes a man 2 to 3 months to make a sperm, then the process constantly renews.
A man’s ejaculation during sexual intercourse releases more than a hundred million sperm, but only about 100 will make it to the proximity of the egg and only one will successfully penetrate the armor of the Zona Pellucida.
Life begins
When the fertilization is successful, the zygote immediately begins developing into an embryo and takes about 3 days to reach the uterus. There, it requires another 3 or more days to implant firmly into the inner lining of the uterus called the Endometrium. Once implanted, the cells that are to become the placenta secrete a hormone, which signals to the ovulated follicle that there is a pregnancy in the uterus. This helps rescue that follicle, now called the Corpus Luteum, from degenerating as it would normally do in that stage of the menstrual cycle.
The Corpus Luteum is responsible for the production of the progesterone required to maintain the pregnancy until 6 to 7 weeks of gestation when the placenta develops and takes over until the baby is born approximately 40 weeks later.
How the Baby is Made in the Lab
In patients undergoing IVF, FSH is administered at levels that are higher than naturally occurring to cause a controlled over-stimulation of the ovaries, so they can ultimately produce multiple eggs. A man will provide a semen sample so that the healthiest sperm can be collected for fertilization. If a male partner is completely infertile, also known as sterile, or the woman doesn’t have a male partner, a donor may be arranged to provide sperm for this process.
Three main procedures of In Vitro Fertilization: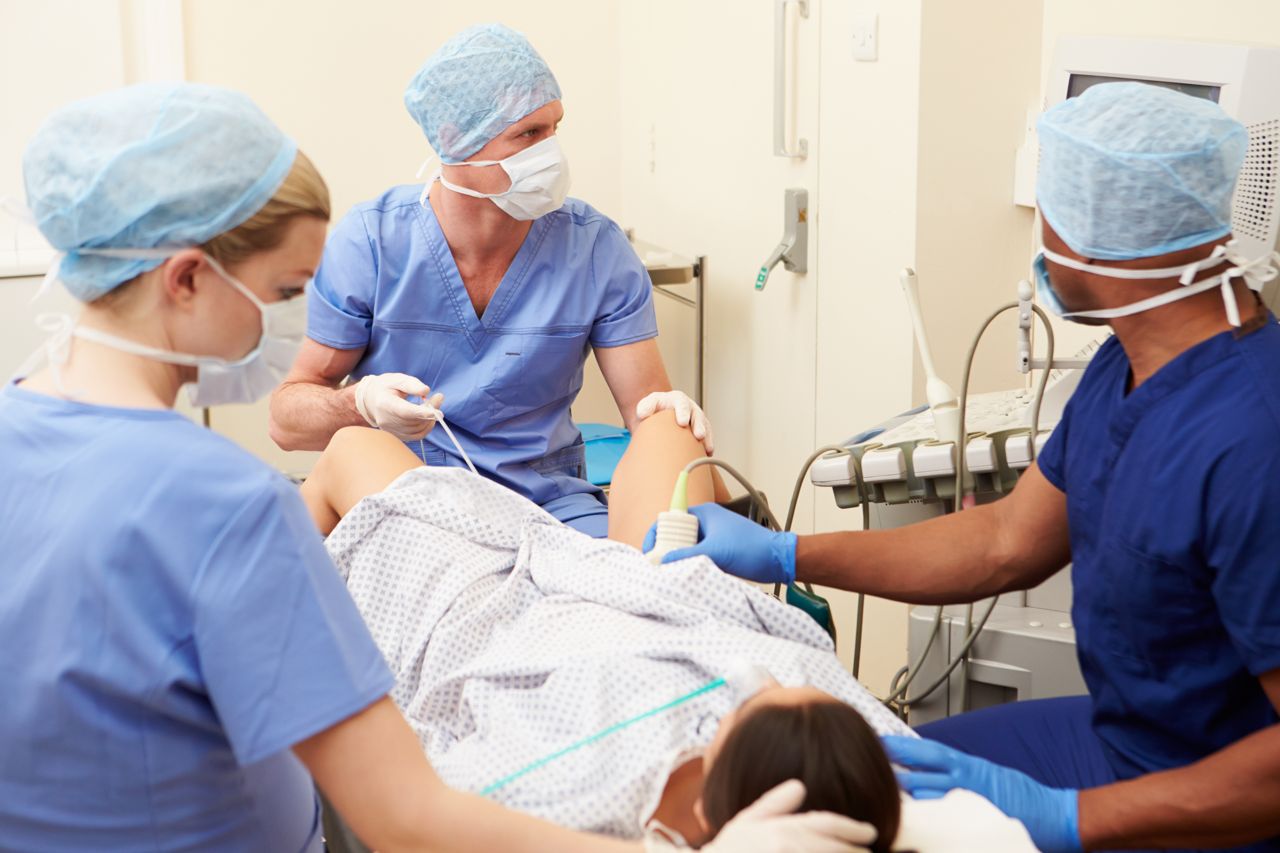
- Follicle Aspiration
- Fertilization
- Embryo Transfer
In the first procedure called Follicle Aspiration, eggs are harvested from the ovaries. An ultrasound probe is then inserted into the woman’s vagina so that her doctor can view her ovaries. Inside the ovaries, the doctor will look for follicles. Each follicle is a fluid-filled sac, which contains an egg. The doctor will then insert a long, thin needle into and through the wall of her vagina and guide it to the ovary. A suction device connected to the needle will collect several eggs from inside their follicles.
In fertilization, the collected eggs will be taken immediately to a laboratory where they will be fertilized. Fertilization may be performed by insemination where several sperms are mixed with the healthiest eggs. The eggs may also be fertilized with the sperm injected directly into them during a process called intracytoplasmic sperm injection.
The fertilized eggs, or embryos, will be monitored for 3 to 5 days as they begin to grow. At this time, the lab may create a hole in the Zona Pellucida surrounding some of the embryos. A process called Assisted Hatching will help these embryos implant in the uterus. Some of the embryos will be used right away for Embryo Transfer and the rest will be stored for future use.
The third procedure of IVF is Embryo Transfer, which is done 3 to 5 days after fertilization. During this procedure, the doctor will insert a tool called speculum into the woman’s vagina to see and check her cervix. He will then load a syringe with a fluid containing one or more of the hatched embryos. The next step is to attach the syringe into thin, long tube known as a catheter. The catheter will be inserted into the vagina, through the cervix, and via the uterus. After it reaches the uterus, the next step is to inject the embryos. The final step is to remove the catheter and speculum.
Who should consider In Vitro Fertilization as an option?
- Women who have been having trouble getting pregnant, a condition known as infertility.
- Women who want to have a child without a male partner
- Women who have one blocked and one open Fallopian tube
- Women who are over the age of 38
Millions of babies who were born from In Vitro Fertilization have had normal, healthy lives. The long-time health consequences of ovarian stimulation with IVF medicines are less clear, but so far, there are no reported side effects. Because of better genetic testing, delayed child-bearing increased accessibility, and diminishing cost, it’s conceivable that baby-making through artificial techniques can outpace natural reproduction in the years to come.
I hope you have find great information about what is IVF or In Vitro Fertilization all about.
[lamoud_Pregnancy_Calculator]My content[lamoud_Pregnancy_Calculator]




