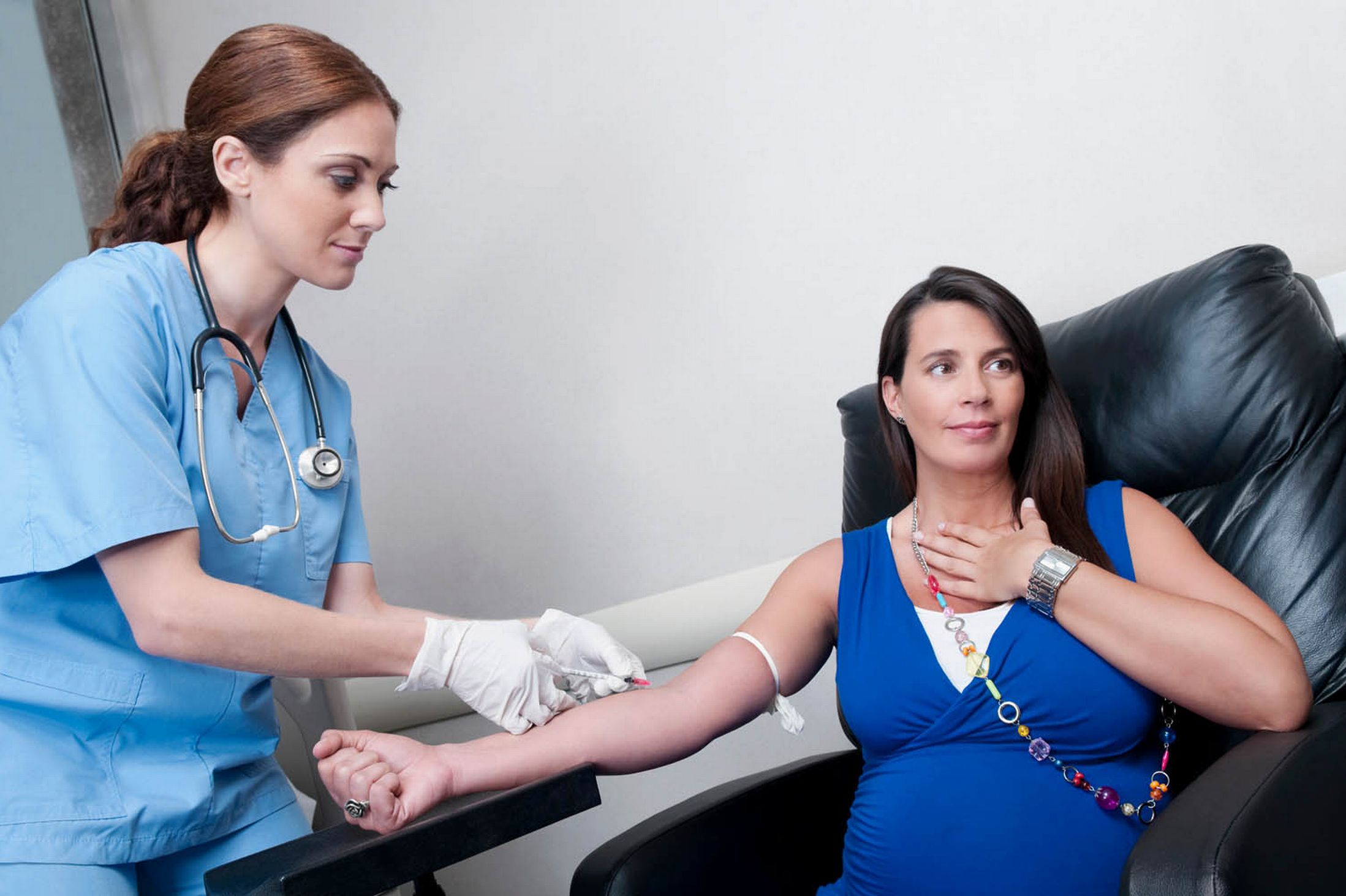
A glucose tolerant test is done in order to check if your body regulates your sugar levels properly. Glucose is the body’s main source of energy and it is found in many foods you eat. The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test or OGTT is used to diagnose gestational diabetes and is offered to pregnant women who are thought to be most likely to develop this condition.
The OGTT is done to determine whether you have or don’t have pregnancy diabetes. Studies have showed that up to 14% of pregnant women develop gestational diabetes. Main reason for developing this kind of diabetes is because your pancreas is not able to produce enough insulin to regulate the amount of sugar in your blood. Not enough insulin results in high sugar level in your body that isn’t immediately necessary for energy.
How is OGTT associated with pregnancy?
During pregnancy your body has to produce extra insulin for both you and your baby’s needs. The need of insulin is increased especially when your baby is growing from about five months. Imagine that all this work for two needs to be done in short amount of time. If your body can’t keep up with the requirements, you may develop diabetes during pregnancy.
Some people use the term ‘Hidden diabetes’ instead of gestational diabetes. It’s the same thing with the exception that they use this term for a reason. This type of diabetes doesn’t show any signs and that’s why OGTT is so important.
What if I am pregnant and not tested for gestational diabetes?
Most pregnant women do not know if they have gestational diabetes. It is a main reason why they are not tested. If you have it and isn’t recognized or treated, you and your baby may be at risk of major complications. A large amount of sugar in your blood can lead to larger baby growth, and this may complicate your vaginal birth. Women who are at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes have:
- a body mass index over 30
- previously given birth to a baby who weighted more than 10lbs.
- had gestational diabetes
- family history with higher prevalence of diabetes
If you feel that you belong in one of these categories, it is recommended that you have an OGTT immediately.
How the OGTT is done?
Unless you have had gestational diabetes before this test is done between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. For women that experienced this before, this test is done twice. It’s done first between 16 weeks and 18 weeks and a second time between 24 weeks and 28 weeks during pregnancy.
Your doctor will tell you how long not to eat and what to drink before the test is done. If you are under any kind of medication therapy you should inform your doctor.
A blood sample will be taken from your vein and used to measure the level of sugar, this is called baseline test. After the first blood sample is provided the nurse will give you a sugary mixture that contains 75g of glucose to drink. You have to drink all of the mixture or if you feel better you can have an energy drink. Another blood sample is taken two hours after drinking the sugary mixture and both samples will be compared to the normal range. The results will arrive in 48 hours.
My Glucose Tolerance Test is positive, now what to do?
The treatment depends on the levels of sugar in your blood. In most cases, this can be put under control with a healthy diet and exercise. Antenatal appointments are important to check on your health and baby’s progress. If your sugar levels are higher this may affect your baby’s development. To avoid major complication you may need to take tablets or insulin injections. To be sure that your blood sugars are back to normal, you may be offered another test six months after your baby is born.
[lamoud_Pregnancy_Calculator]My content[lamoud_Pregnancy_Calculator]